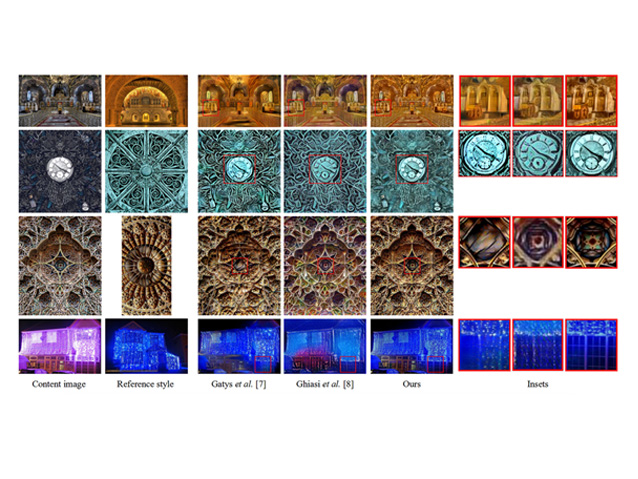
Image style transfer has attracted much attention in recent years. However, results produced by existing works still have lots of distortions. This paper investigates the CNN-based artistic style transfer work specifically and finds out the key reasons for distortion coming from twofold: the loss of spatial structures of content image during content-preserving process and unexpected […]