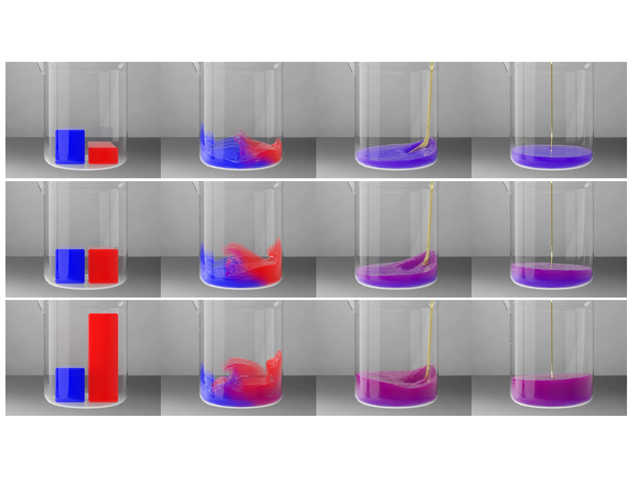
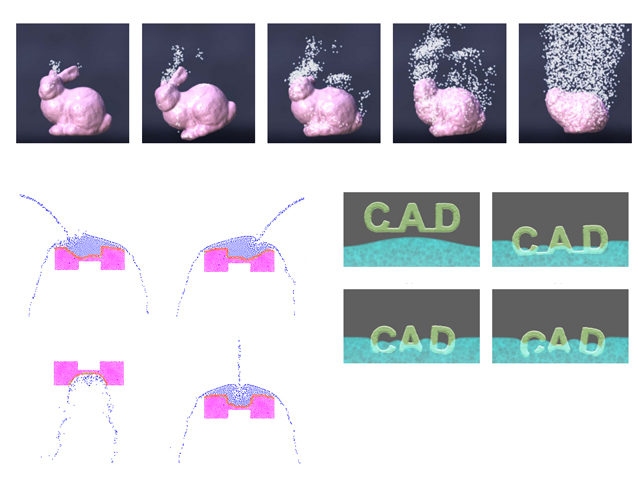
A novel unified particle-based method is proposed for real-time dissolution simulation that is fast, predictable, independent of sampling resolution, and visually plausible. The dissolution model is derived from collision theory and integrated into a smoothed particle hydrodynamics fluid solver. Dissolution occurs when a solute is submerged in solvent. Physical laws govern the local excitation of […]